Innovations in Textile Machinery For Agrotextiles
Share Post
Spunbond Nonwoven Technology: Spunbond technology refers to the direct conversion of polymers into nonwoven fabric using an integrated process of extrusion, spinning, and web formation. It starts with melting a thermoplastic polymer, usually polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), or polylactic acid (PLA), and extruding it through spinnerets to form continuous filaments. These filaments are then laid into a web and bonded using thermal or mechanical means. The following table summarizes the steps involved in the spunbond process and how it translates to agrotextile applications:
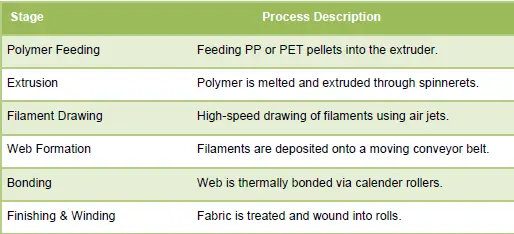
Recent technological improvements have made spunbond lines more versatile and suitable for agrotextiles. Twinbeam or multi-beam spunbond machines allow the production of multilayer fabrics with varied properties. Some of the Major Advancements Include:
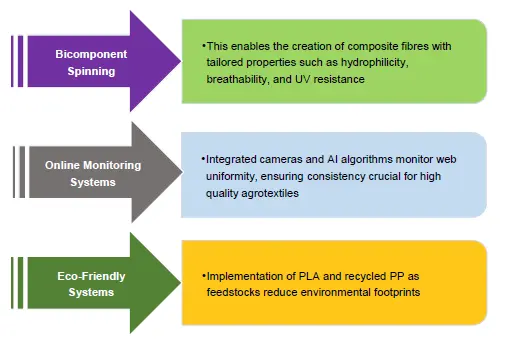
Spunbond Nonwoven Technology Applications in Agrotextiles
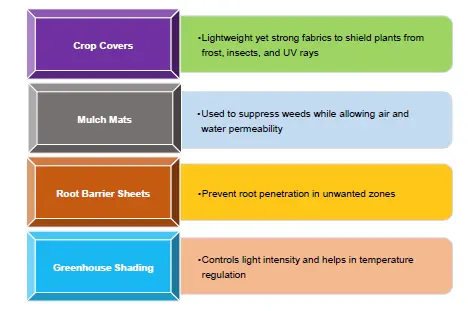
Properties of Spunbond Agrotextiles
A large-scale agrotextile plant based in India utilizes a double-beam spunbond line to produce biodegradable mulch mats. These mats are embedded with natural additives for pest resistance and have a service life of 6–8 months. The incorporation of meltblown layers in between the spunbond layers enhances filtration and thermal insulation, ideal for soil conditioning.
Needle Punching Technology: Needle punching involves mechanically interlocking fibres using barbed needles that repeatedly punch through the loose fibre web. This process results in a strong, flexible, and breathable fabric. It can process both synthetic and natural fibres, making it ideal for a wide range of agrotextile applications. Process Flow from Needle Punching to Agrotextile:
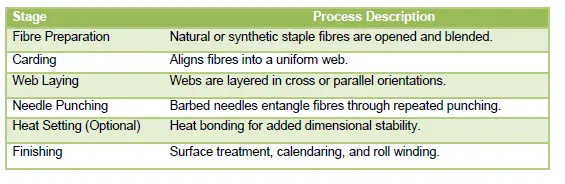
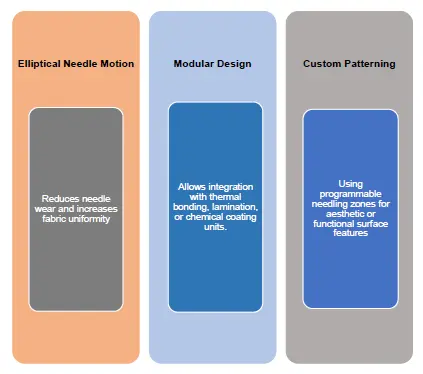
Technological Advancements in Needle Punching Machines
Modern needle punching lines are capable of high-speed, high-volume production with advanced features such as:
Needle-punched nonwovens are widely used in the following agricultural functions:
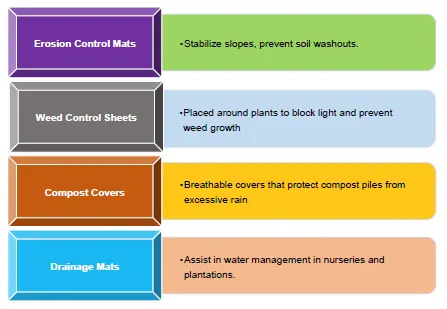
Properties of Needle-Punched Agrotextiles

A European textile company employs needle punching lines with high-density needle boards to produce erosion control mats. These mats are made using a blend of jute and PP fibres. The company integrates post-needling calendaring and surface treatments to enhance resistance against microbial degradation and UV exposure. The final product is used extensively along riverbanks and in terraced agriculture.
The use of advanced nonwoven machinery like Spunbond and Needle Punching technologies has revolutionized agrotextile production. These machines not only ensure high-speed, large-scale production but also deliver fabrics tailored to the complex needs of modern agriculture. With ongoing innovation and the increasing integration of eco-friendly materials and AI-based quality monitoring, the future of agrotextile manufacturing is promising, sustainable, and technologically robust.
From soil protection to crop enhancement, nonwoven agrotextiles are becoming indispensable to sustainable farming, thanks largely to the innovations in textile machinery. As the global agricultural sector moves toward climate resilience and sustainability, these technologies will form the backbone of agricultural fabric solutions.
03:34 PM, Oct 14







.webp)


















1.jpg)
1.jpg)



